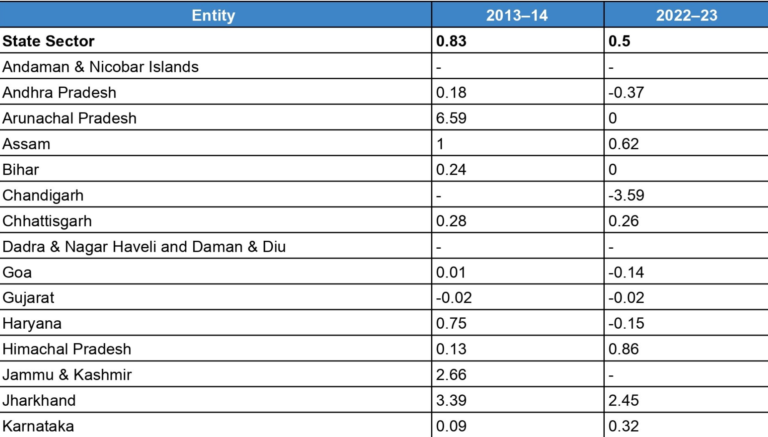
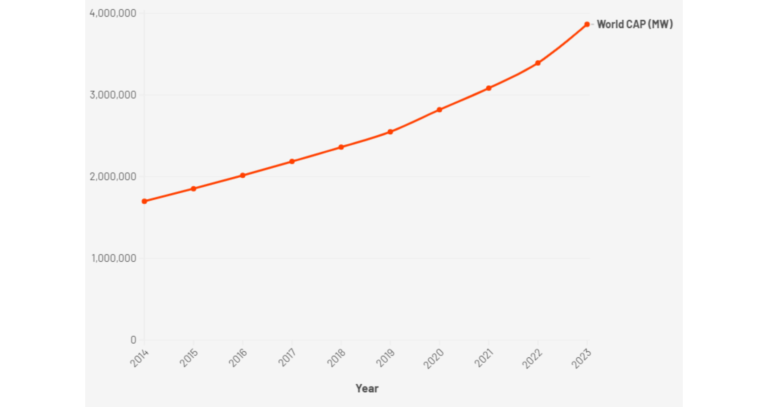
Draft NEP 2026 signals a decisive shift in India’s power sector priorities
India’s power sector has moved beyond the challenge of access. With near-universal electrification achieved, policy focus has shifted to reliability, affordability, sustainability, and system resilience. The Ministry of Power’s Draft National Electricity Policy (NEP) 2026 marks a clear departure from the access-led framework of NEP 2005 and aligns electricity planning with the long-term objective of Viksit Bharat @ 2047. The draft policy is not a routine revision. It reframes electricity from a capacity expansion problem…