10,273 ckm of Lines and 71,197 MVA Added: T&D in 2024
Author: PPD Team Date: January 6, 2025

Year-end review: Power transmission and distribution in India
National Electricity Plan 2023-2032
The Government of India has finalized the National Electricity Plan for the period 2023-2032 to address a projected peak demand of 458 GW by 2032, with an estimated total investment of Rs 9.15 trillion.
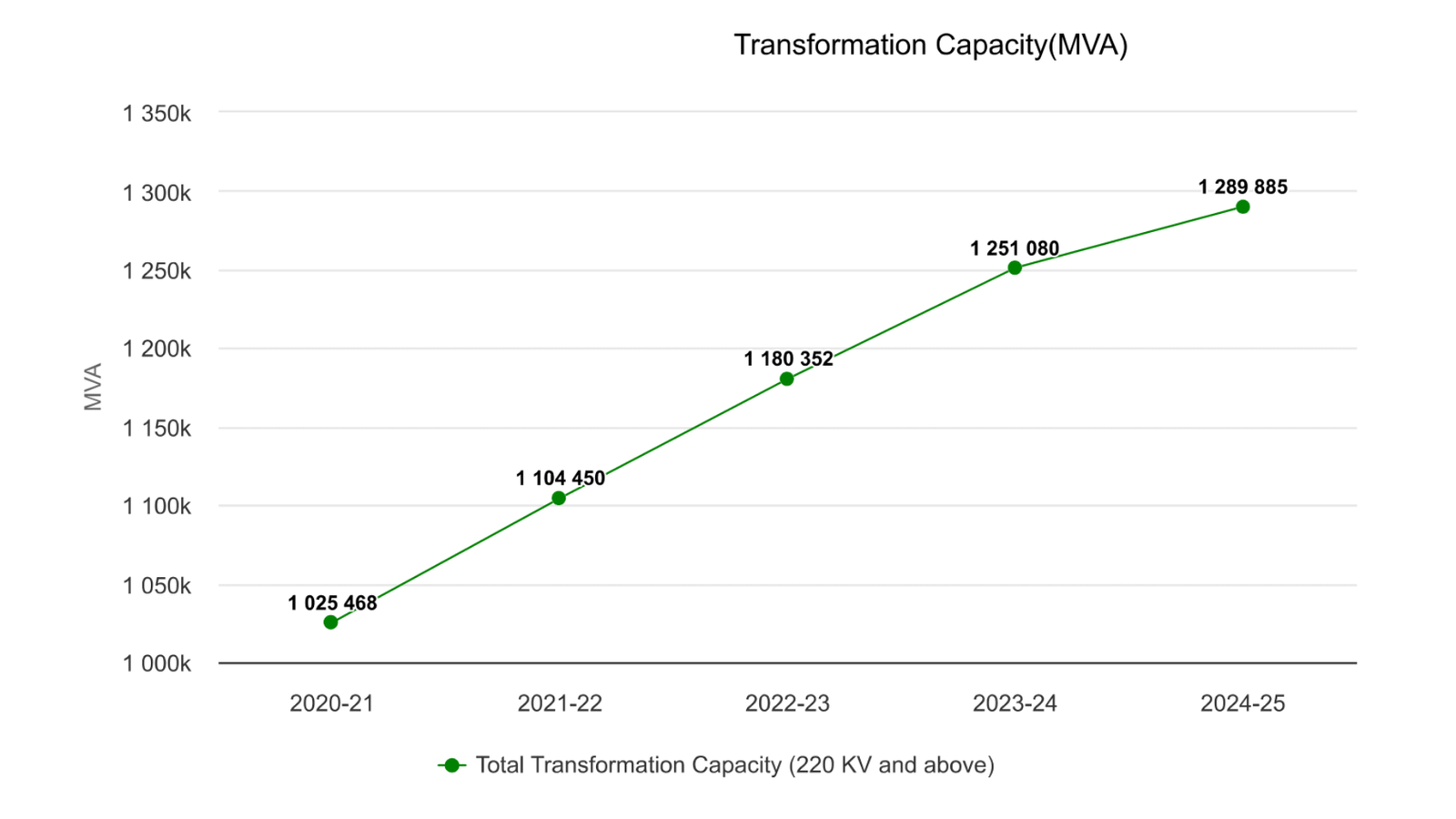
In the new plan, the transmission network will grow from 491,000 ckm in 2024 to 648,000 ckm by 2032, while transformation capacity will increase from 1,290 GVA to 2,342 GVA.
Additionally, nine new High Voltage Direct Current (HVDC) lines with a combined capacity of 33.25 GW will supplement the 33.5 GW already operational. Inter-regional transfer capacity will expand from 119 GW to 168 GW, and the plan will cover transmission systems of 220 kV and above.
Approval of 50 GW ISTS Capacity
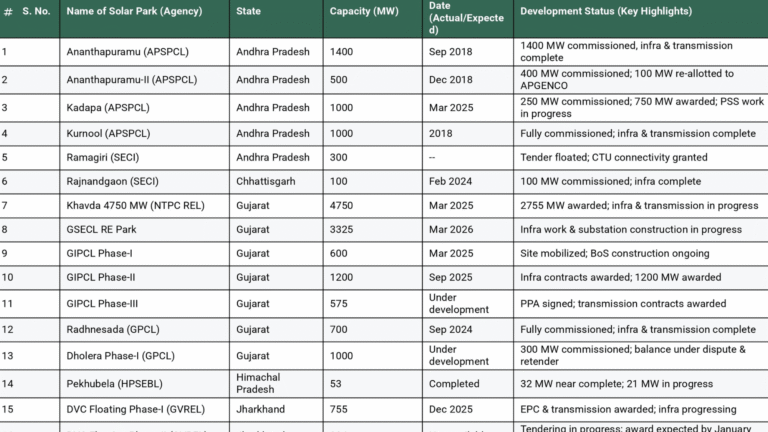
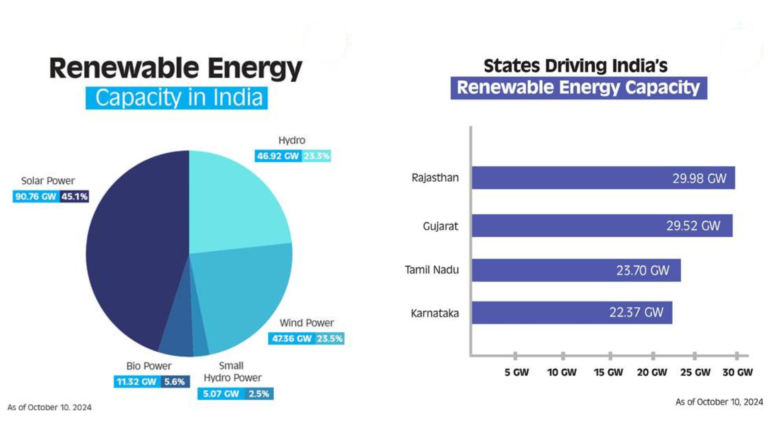
The government has approved 50.9 GW of inter-state transmission projects at Rs 606.76 billion. These projects are part of the strategy to connect 280 GW of variable renewable energy (VRE) to the inter-state transmission system (ISTS) by 2030. Out of the total planned network of 335 GW, 42 GW has been completed, 85 GW is under construction, and 75 GW is under bidding. The remaining 82 GW will be approved in subsequent phases.
Transmission System Enhancements in 2024
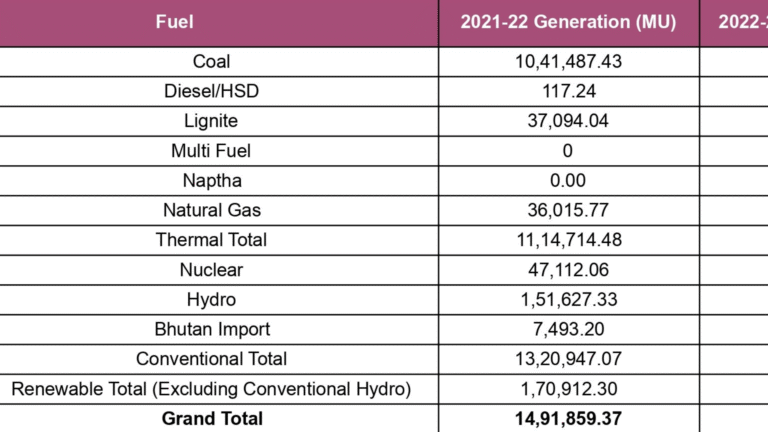
In 2024, 10,273 ckm of transmission lines (220 kV and above), 71,197 Mega Volt Ampere (MVA) of transformation capacity, and 2,200 MW of inter-regional transfer capacity were added to India’s transmission infrastructure.
Revised Right of Way Guidelines
To expedite the development of power transmission infrastructure for evacuating 500 GW of renewable energy by 2030, the Ministry of Power revised the Right of Way (RoW) guidelines in June 2024. Compensation for tower base areas has been increased from 85% to 200% of the land value, while for the RoW corridor, compensation has been raised from 15% to 30%.
Revamped Distribution Sector Scheme (RDSS)
Under the Revamped Distribution Sector Scheme (RDSS), designed to enhance operational efficiency and financial sustainability of distribution companies (Discoms), significant progress was made.
Key achievements include the sanctioning of:
- 197.9 million prepaid smart meters,
- 5.25 million distribution transformer (DT) meters, and
- 210,704 feeder meters at Rs 1.31 trillion.
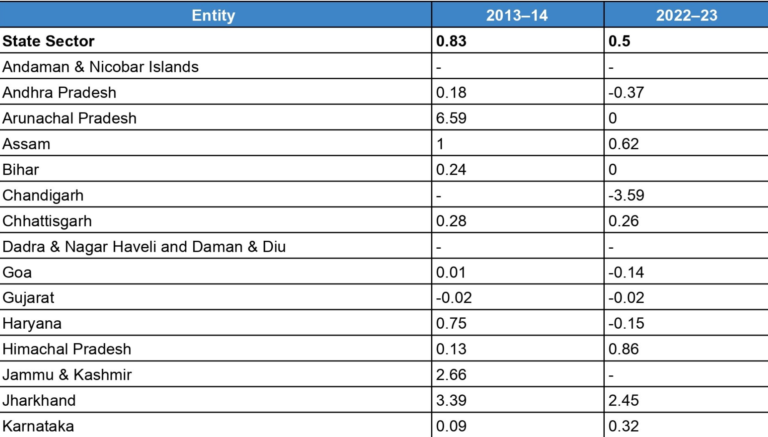
Loss reduction works worth Rs 1.46 trillion were approved, with Rs 183.79 billion already disbursed. As a result, aggregate technical and commercial (AT&C) losses were reduced to 15.37%, and the Average Cost of Supply-Average Revenue Realized (ACS-ARR) gap narrowed to Rs 0.45/kWh in FY2023.
Through initiatives like PM-JANMAN (Pradhan Mantri Janjati Adivasi Nyaya Maha Abhiyan) and DA-JGUA (Dharti Aaba Janjatiya Gram Utkarsh Abhiyan), Rs 43.55 billion has been allocated to electrify 961,419 households, including those from Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups (PVTGs) and tribal areas, alongside public spaces identified under DA-JGUA.
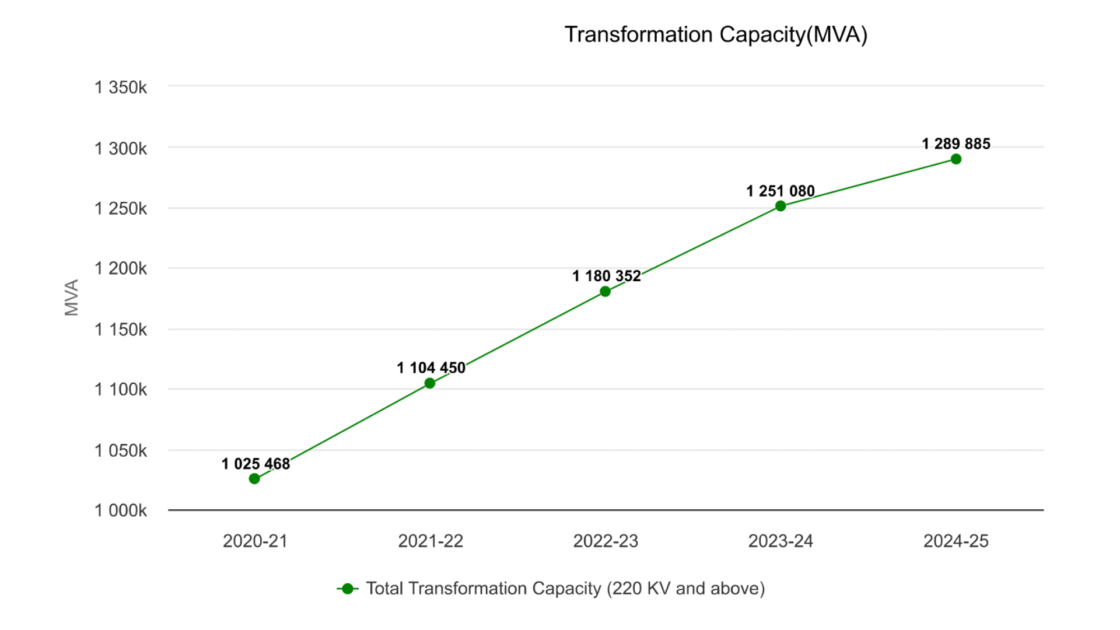
Photo credit: National Power Portal (NPP); Source of information: Press Information Bureau (PIB)