CEA releases roadmap to 100 GW pumped storage by 2035–36
Author: PPD Team Date: January 27, 2026
The Central Electricity Authority (CEA) has released a roadmap outlining how India plans to achieve 100 GW of Hydro Pumped Storage Projects capacity by 2035–36. Along with capacity projections, the document sets out policy, regulatory and financial measures to accelerate project development and improve viability.
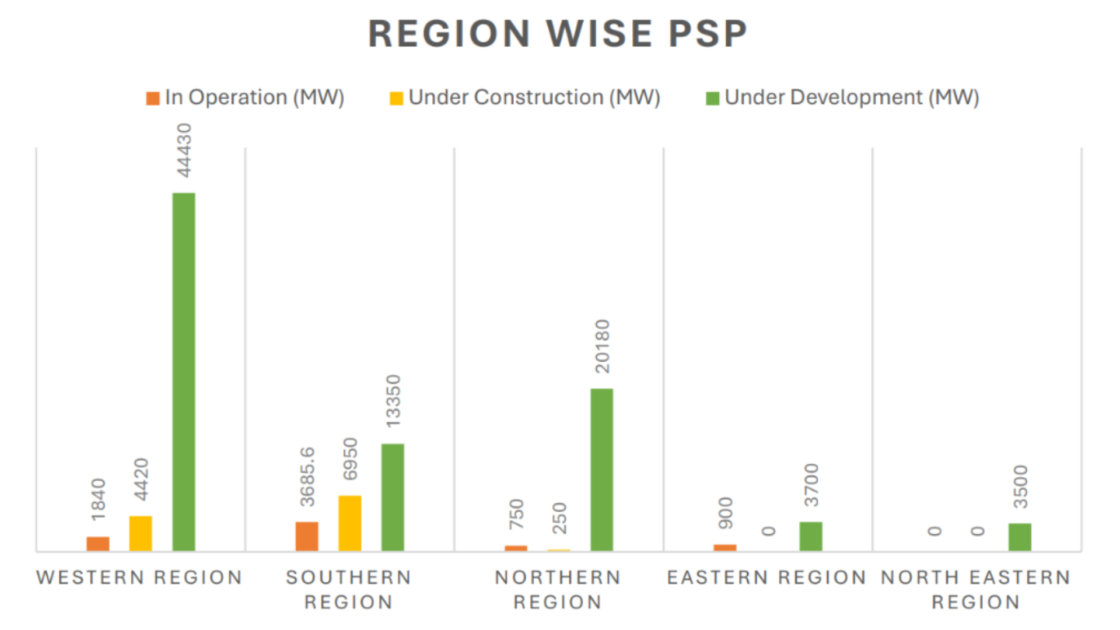
The roadmap projects cumulative PSP capacity of about 100,810 MW by 2035–36, including 11,620 MW already under construction. It highlights off-stream closed-loop PSPs as a key driver due to their lower environmental impact and shorter gestation period, typically around 3.5 to 4 years.
As of December 31, 2025, India has 10 operational PSPs with an installed capacity of 7,175.6 MW. Another 10 projects with 11,620 MW are under construction. Projects totalling 9,580 MW have received concurrence from the CEA but are yet to start construction, while 54 projects with 74,940 MW are at the survey and investigation stage, most of them off-stream closed-loop schemes.
To enable faster deployment, the roadmap lists several measures. These include tariff-based competitive bidding guidelines for the procurement of storage capacity or stored energy from pumped storage plants, notified in February 2025. It also provides for waiver of inter-state transmission system charges for PSPs, aimed at reducing delivered power costs and improving commercial viability.
The document calls for budgetary support towards enabling infrastructure such as access roads and transmission connectivity, which often add significantly to upfront costs. It also proposes the enhancement of the threshold limit for concurrence of PSPs by the CEA under ease of doing business reforms, to reduce approval timelines.
Other measures include guidelines for formulation, examination and concurrence of detailed project reports, promotion of off-stream closed-loop PSPs as a distinct category, and allowing the use of exhausted mines for developing pumped storage projects. The roadmap also links PSP deployment with Energy Consumption Obligation and long-term Resource Adequacy planning to ensure demand for long-duration storage beyond 2030.
According to CEA studies, all-India storage capacity requirements are projected to rise to 161 GW by 2034–35 and 476 GW by 2046–47, driven by higher renewable energy penetration. The roadmap positions PSPs as the primary solution for long-duration storage, grid stability, frequency regulation and peak power support over this period.
Graph: Region-wise pumped storage capacity in India. Credit: Central Electricity Authority roadmap on Hydro Pumped Storage Projects (January 2026)

